Oil’s Ripple Through the Middle East
Hidden under the desert of the Middle East lay a treasure responsible for rewriting the region's poor destiny. The Middle East was recognized as a remote and secluded desert area, until the area rose to fame due to its significant financial uprise from the oil business. The people of the area pursued a rural like lifestyle, but as the oil industry stimulated development, it led to the employment of many spurring the urbanisation of the area. This region was once unknown due to the lack of having any strong political and international relationships, until the discovery of oil in 1908. Following this revolutionary discovery, various countries become keen to develop closer relationships and partnerships towards the Middle East (Ice.org). The Middle East was once an uninhabited and remote desert region, until the transformative discovery of oil which had propelled its financial, social, and political progress.
The Middle East’s Financial Engine
The discovery of oil after World War II allowed for the region's economy to thrive significantly, especially in the shift from it being an LDC (Least Developed Countries) towards an MDC (More Developed Countries). Before the oil boom, the Middle East was extremely underdeveloped where it faced issues such as minimal transport, water, and sewage systems. The discovery of oil led to the development in all these industries which were the stepping stones into the shift towards the MDC status. In this transition to an MDC, made possible by the oil business, the Middle East was able to fund many regions during the periods of 1950 to 1960 (similar to the Victorian era’s impact in Britian). If oil were not to be discovered in 1908 in the Middle East, many of the developments would be delayed as other countries such as Kazakhstan would have discovered oil first. Kazakhstan holds the amount to produce 300 billion barrels of oil, whereas the Middle East holds 200 billion barrels of oil, however the Middle East still holds immense control in this market as they hold the credibility of discovering this resource first (Ice.org). The oil business helped the Middle East to thrive, as this helped in branching out to new ways for the economy to prosper.
Within the Middle East
Within the Middle East there are several countries, and each is on a different level of the MDC status, where these rankings are based upon on how each country strategically used oil for their benefit. Kuwait, Iran, Iraq, and Saudi Arabia are among the countries that were able to take advantage of oil production. Oil revenue was used for improving water supplies through creating dams, irrigation systems, and desalination plants (Ice.org). Saudi Arabia, one of the “prime players” in this business, produces over 12 million barrels of oil per day, which is nearly 12% of the world’s output. Within these before mentioned countries are where the headquarters of Saudi Aramco, WOOD, ADNOC, AlMansooria, and Petrofac international (five of the top ten oil producing businesses) are located, responsible for over 27% of the world’s production (Carpenter). This transformation from a remote unknown region to a global superpower was possible through the region’s rapid economic development from oil, yet it also rose to power due to its impact socially.
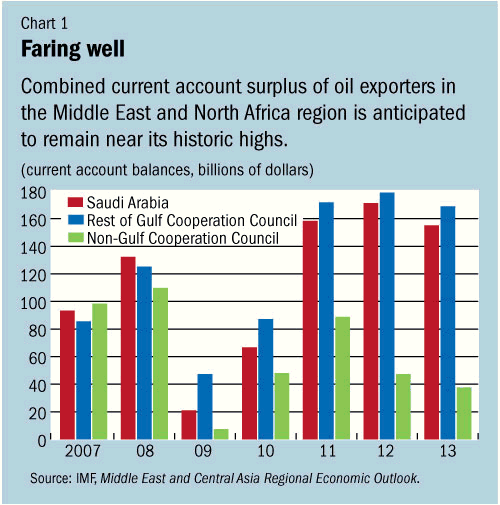
The Ripples of Oil, Societal Transformations
A nation’s pride and power comes from its people, and the Middle East was able to show its gratitude towards the public by investing back in the people of the region. Oil and gas industries created many employment opportunities, both directly and indirectly (Carpenter). Oil wealth had led to significant gains socially with outcomes such as reductions in infant mortality rate, increased life expectancy, and higher literacy rates (Malachova, 2012).
"The result has been increased economic prosperity, a revitalized manufacturing sector, improvement of millions of lives through direct and indirect employment and lower energy costs, new sources of government revenues, and strengthened energy security for the nation. Other benefits exist which cannot be measured with hard numbers. For example, the industry’s support for millions of jobs enables workers to have better access to health care for themselves and their families. Similarly, new or renewed economic vitality in a location or region can reduce the societal risks associated with economic distress." (XtoEnergy)
The oil rich nations within the Middle East were able to provide their population with many goods and services such as education, health, and employment, thus leading to the improved living conditions and standards (Eazy Explainer, 2022). With the nation reinvesting back in its citizen’s wellbeing, the public in return supports the nation politically by aiding in the creation of peace, receiving global recognition, and further on.
Oil Fuelling Politics
The countries in the Middle East have significant political influence regionally and globally due to their control over one of the world’s essential resources, oil. With these countries having this immense influence over the oil business, they were able to shape their international relations (World Economic Forum). Arab governments have been able to use oil as leverage within negotiations between the USA and themselves. With this power over international negotiations, the Middle East is able to easily sway foreign governments into agreeing to anything in accordance to their liking (Prezi.com, 2012). This production and distribution of oil has helped in the elevation of the Middle East’s importance in global politics, thus developing the region’s public reputation. Oil has been able to bring a major impact towards the Middle East politically, specifically due to the rapid and continuous growth seen in these regions (Imf.org, 2012).
With the empowerment politically, the Middle East was able to thrive, especially with the government gaining a substantial amount of power as the years pass. Oil profits have allowed governments to maintain internal stability through social programs. These profits have also been allocated to maintain internal stability through subsidies, which ultimately contributes to the political success (Carpenter). Holding considerable control and yielding substantial profits through oil has caused a shift in political powers, from a corrupt government towards a stronger and neo-traditional monarchy (Eazy Explainer, 2022). The political landscape has been significantly shaped by the impacts brought by oil production, which has led to the region continuing to prosper.


Oil’s Shadow on the Middle East
Although the Middle East has been able to rise from an LDC due to its advancement financially, socially, and politically from oil, with this came several minor conflicts. The economic impact from oil brought in great fortune towards those in the middle and upper class, but the lower class had continued to face more challenges, thus leading to wealth disparities (Carpenter). Another conflict caused by oil discovery is how a significant amount of western interest came to be drawn in, which had impacted the conflicts involving the region’s political borders (Anderson, 2014). With issues involving political borders come the conspiracies of how oil revenue has been said to fund terrorist acts in Syria, Iraq, and Yemen through illegal organizations and institutions (Prezi.com, 2012). With the many advantages that came from the impact in these three sectors of the regions, similarly, arrived many disadvantages; nonetheless the region was able to face these challenges and still become the global superpower it is today.
Oil, the black gold of the world, has greatly benefited the Middle East. In the absence of this revolutionary discovery, the Middle East would remain to be the same unknown area it used to be. The oil business helped in the advancement of the Middle East in many areas. Financially, it was able to develop rapidly due to how oil influenced the creation of many sources of income, directly and indirectly. Additionally, the public benefited as the oil business led to the area having a high standard of life. Income from oil is not solely invested into the public, but also benefits the region politically. Oil was the key for the Middle East to develop strong political ties and receive global recognition. The revolutionary discovery of oil empowered the Middle East financially, socially, and politically. With the development in these areas, it led to the region prospering and becoming the nations as we know them today. Ultimately, oil has significantly influenced and shaped the Middle East’s uprising, where it successfully established itself as a dominant player in the oil business worldwide.
Works Cited
Al-Rasheed, Madawi, et al. “Oil and the Geopolitics of Empire in the Middle East.” Catalyst, 9 Jan. 2022, catalyst-journal.com/2022/09/oil-and-the-geopolitics-of-empire-in-the-middle-east. Accessed 06 Mar. 2024.
Anderson, Scott. Lawrence in Arabia: War, Deceit, Imperial Folly and the Making of the Modern Middle East. Atlantic Books, 2014.
Bishara, Marwan. “Middle East Politics: From Hyper to Hybrid.” Al Jazeera, 21 July 2022, www.aljazeera.com/opinions/2022/7/21/the-middle-east-from-hyper-to-hybrid. Accessed 06 Mar. 2024.
Carpenter, J. William. “The Biggest Oil Producers in the Middle East.” Investopedia, www.investopedia.com/articles/investing/101515/biggest-oil-producers-middle-east.asp#:~:text=Saudi%20Arabia&text=Many%20of%20the%20largest%20oil,roughly%2015%25%20of%20global%20output. Accessed 04 Mar. 2024.
“How Do Arab Countries Have the Largest Oil Reserves?” YouTube, 17 Aug. 2022, www.youtube.com/watch?v=dCGGu8Ngu4o&t=6s. Accessed 04 Mar. 2024.
Malachova, Anastasija. “The Middle East and Oil: Economic Modernisation and Political Stagnation.” E, 30 Oct. 2012, www.e-ir.info/2012/10/29/the-middle-east-and-oil-economic-modernisation-and-political-stagnation/. Accessed 04 Mar. 2024.
Moen, John. “Middle East Map / Map of the Middle East - Facts, Geography, History of the Middle East.” WorldAtlas, 25 Apr. 2017, www.worldatlas.com/webimage/countrys/me.htm. Accessed 06 Mar. 2024.
Oil Development in the Middle East | Institution of Civil Engineers, www.ice.org.uk/what-is-civil-engineering/what-do-civil-engineers-do/oil-development-in-the-middle-east. Accessed 04 Mar. 2024.
“The Changing Geopolitics of Oil in the Middle East.” World Economic Forum, www.weforum.org/agenda/2015/06/the-changing-geopolitics-of-oil-in-the-middle-east/#:~:text=URL%3A%20https%3A%2F%2Fwww.weforum.org%2Fagenda%2F2015%2F06%2Fthe. Accessed 04 Mar. 2024.
(PDF) Literacy and Life Expectancy, www.researchgate.net/publication/328539041_Literacy_and_life_expectancy. Accessed 06 Mar. 2024.
Survey, IMF. “IMF Survey: Middle East Economies Post Divergent Performance.” IMF, 11 Nov. 2012, www.imf.org/en/News/Articles/2015/09/28/04/53/socar110912a. Accessed 06 Mar. 2024.
“What Impact Did Oil Have on the Middle East.” Prezi.Com, prezi.com/pyf2ovddosao/what-impact-did-oil-have-on-the-middle-east/#:~:text=POLITICAL%20IMPACT%20OF%20OIL%20IN,and%20other%20aspects%20of%20life. 2012 Accessed 04 Mar. 2024.